-
Python Write To File카테고리 없음 2020. 1. 24. 01:06

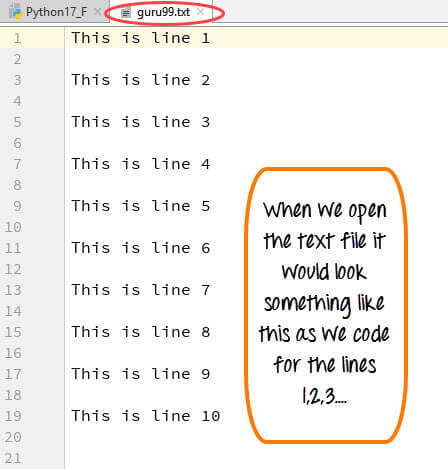
In Python, there is no need for importing external library to read and write files. Python provides an inbuilt function for creating, writing and reading files. In this tutorial, we will learn. How to Create a Text File. How to Append Data to a File. How to Read a File. How to Read a File line by line. File Modes in Python. If you want to save a dictionary to a json file. Save dictionary to text file (raw,.txt) You can save your dictionary to a text file using the code below: save dictionary to a pickle file (.pkl) The pickle module may be used to save dictionaries (or other objects) to a file. The module can serialize and deserialize Python objects. Python File Handling Operations. Most importantly there are 4 types of operations that can be handled by Python on files: Open; Read; Write; Close; Other operations include: Rename; Delete; Python Create and Open a File. Python has an in-built function called open to open a file. It takes a minimum of one argument as mentioned in the below syntax.
Python Write To File Using With
This chapter covers all the basic I/O functions available in Python. For more functions, please refer to standard Python documentation. Printing to the ScreenThe simplest way to produce output is using the print statement where you can pass zero or more expressions separated by commas. This function converts the expressions you pass into a string and writes the result to standard output as follows −#!/usr/bin/pythonprint 'Python is really a great language,', 'isn't it?' This produces the following result on your standard screen −Python is really a great language, isn't it?Reading Keyboard InputPython provides two built-in functions to read a line of text from standard input, which by default comes from the keyboard.
Python Write To File With Statement
These functions are −. rawinput. inputThe rawinput FunctionThe rawinput(prompt) function reads one line from standard input and returns it as a string (removing the trailing newline).#!/usr/bin/pythonstr = rawinput('Enter your input: ');print 'Received input is: ', strThis prompts you to enter any string and it would display same string on the screen. When I typed 'Hello Python!'
, its output is like this −Enter your input: Hello PythonReceived input is: Hello PythonThe input FunctionThe input(prompt) function is equivalent to rawinput, except that it assumes the input is a valid Python expression and returns the evaluated result to you.#!/usr/bin/pythonstr = input('Enter your input: ');print 'Received input is: ', strThis would produce the following result against the entered input −Enter your input: x.5 for x in range(2,10,2)Recieved input is: 10, 20, 30, 40Opening and Closing FilesUntil now, you have been reading and writing to the standard input and output. Now, we will see how to use actual data files.Python provides basic functions and methods necessary to manipulate files by default. You can do most of the file manipulation using a file object. The open FunctionBefore you can read or write a file, you have to open it using Python's built-in open function. This function creates a file object, which would be utilized to call other support methods associated with it. Syntaxfile object = open(filename , accessmode, buffering)Here are parameter details −.filename − The filename argument is a string value that contains the name of the file that you want to access.accessmode − The accessmode determines the mode in which the file has to be opened, i.e., read, write, append, etc. A complete list of possible values is given below in the table.
This is optional parameter and the default file access mode is read (r).buffering − If the buffering value is set to 0, no buffering takes place. If the buffering value is 1, line buffering is performed while accessing a file. If you specify the buffering value as an integer greater than 1, then buffering action is performed with the indicated buffer size. If negative, the buffer size is the system default(default behavior).Here is a list of the different modes of opening a file − Sr.No.Modes & Description1rOpens a file for reading only. The file pointer is placed at the beginning of the file.
This is the default mode.2rbOpens a file for reading only in binary format. The file pointer is placed at the beginning of the file. This is the default mode.3r+Opens a file for both reading and writing. The file pointer placed at the beginning of the file.4rb+Opens a file for both reading and writing in binary format. The file pointer placed at the beginning of the file.5wOpens a file for writing only. Overwrites the file if the file exists. If the file does not exist, creates a new file for writing.6wbOpens a file for writing only in binary format.
Overwrites the file if the file exists. If the file does not exist, creates a new file for writing.7w+Opens a file for both writing and reading. Overwrites the existing file if the file exists.
If the file does not exist, creates a new file for reading and writing.8wb+Opens a file for both writing and reading in binary format. Overwrites the existing file if the file exists. If the file does not exist, creates a new file for reading and writing.9aOpens a file for appending.
The file pointer is at the end of the file if the file exists. That is, the file is in the append mode. If the file does not exist, it creates a new file for writing.10abOpens a file for appending in binary format. The file pointer is at the end of the file if the file exists.
Python Write To File Csv
That is, the file is in the append mode. If the file does not exist, it creates a new file for writing.11a+Opens a file for both appending and reading. The file pointer is at the end of the file if the file exists. The file opens in the append mode. If the file does not exist, it creates a new file for reading and writing.12ab+Opens a file for both appending and reading in binary format.
The file pointer is at the end of the file if the file exists. The file opens in the append mode.
